What is Google Bard? Everything you need to know about the ChatGPT rival

What is Google Bard? Everything you need to know about the ChatGPT rival
Google finally joined the AI race and launched a ChatGPT rival called Bard – an “experimental conversational AI service” earlier this year. Google Bard is an AI-powered chatbot that acts as a poet, a crude mathematician and a even decent conversationalist.
The chatbot is similar to ChatGPT in many ways, able to answer complex questions about the universe and give you a deep dive into a range of topics in a conversational, easygoing way. The bot, however, differs from its rival as it’s connected to the web and therefore, according to Google gives “fresh, high-quality responses”.
Google Bard is powered by LaMDA (short for Language Model for Dialogue Applications). Like ChatGPT, it’s a type of machine learning called a ‘large language model’ that’s been trained on a vast dataset and is capable of understanding human language as it’s written.
Google I/O 2023
Google I/O 2023, an event in which the tech giant dives into the upcoming features, gadgets, and updates across its product line, revealed a ton of new information about Bard, Google’s artificial intelligence (AI)-powered chatbot.
Though we initially found Bard to fall short in terms of features and performance compared to its competitors, Google announced new tools that will round out the experience much better and make it far more competitive to other AI chatbots like ChatGPT and Microsoft Bing.
The I/O event revealed several new features coming now and soon including Google PaLM 2, improved citations, export capabilities to Google Docs and Gmail, an export tool that will allow users to export Python code through Replit, increase language support to 40 languages, multimodal functionality, a wide variety of Adobe integrations, and more.
ChatGPT and Microsoft Bing are dominating the AI sphere, but we hope to see Bard catch up, and hopefully, with these additions, Bard can truly challenge the big dogs of the AI chatbot world. We hope to see Bard’s logical capabilities improve so that it can match ChatGPT and Bing when it comes to coding and logical reasoning — basically being able to arrive at an answer or conclusion using set facts or data. It would also help kick Bard into the big leagues if we saw an improved search engine integration.

So what exactly will Google’s Bard do for you and how will it compared with ChatGPT, which Microsoft appears to be building into its own search engine, Bing? Here’s everything you need to know about it.
What is Google Bard?
Like ChatGPT, Bard is a chatbot that’s built on deep learning algorithms called ‘large language models’, in this case one called LaMDA.
To start with, Bard has been released on a “lightweight model version” of LaMDA. Google says this allows it to scale the chatbot to more people, as this “much smaller model requires significantly less computing power”.
As of now, Bard is no longer in a testing phase, having officially left the waitlist. It’s now available in over 180 countries, and users can even join using a Workspace account instead of a personal Google account.
Google combined external feedback with its own internal testing. This is because, for all their benefits, chatbots have also shown a propensity for negative traits that include everything from bias to powering cyberattacks.
Opening up chatbots for public testing brings great benefits that Google says it’s “excited” about, but also risks that explain why the search giant has been so cautious to release Bard into the wild. The meteoric rise of ChatGPT has, though, seemingly forced its hand and expedited the public launch of Bard.
What will Google’s Bard let you do?
Until recently, Google has been a little vague about Bard’s capabilities but in short, Bard is a next-gen development of Google Search that could change the way we use search engines and look for information on the web.
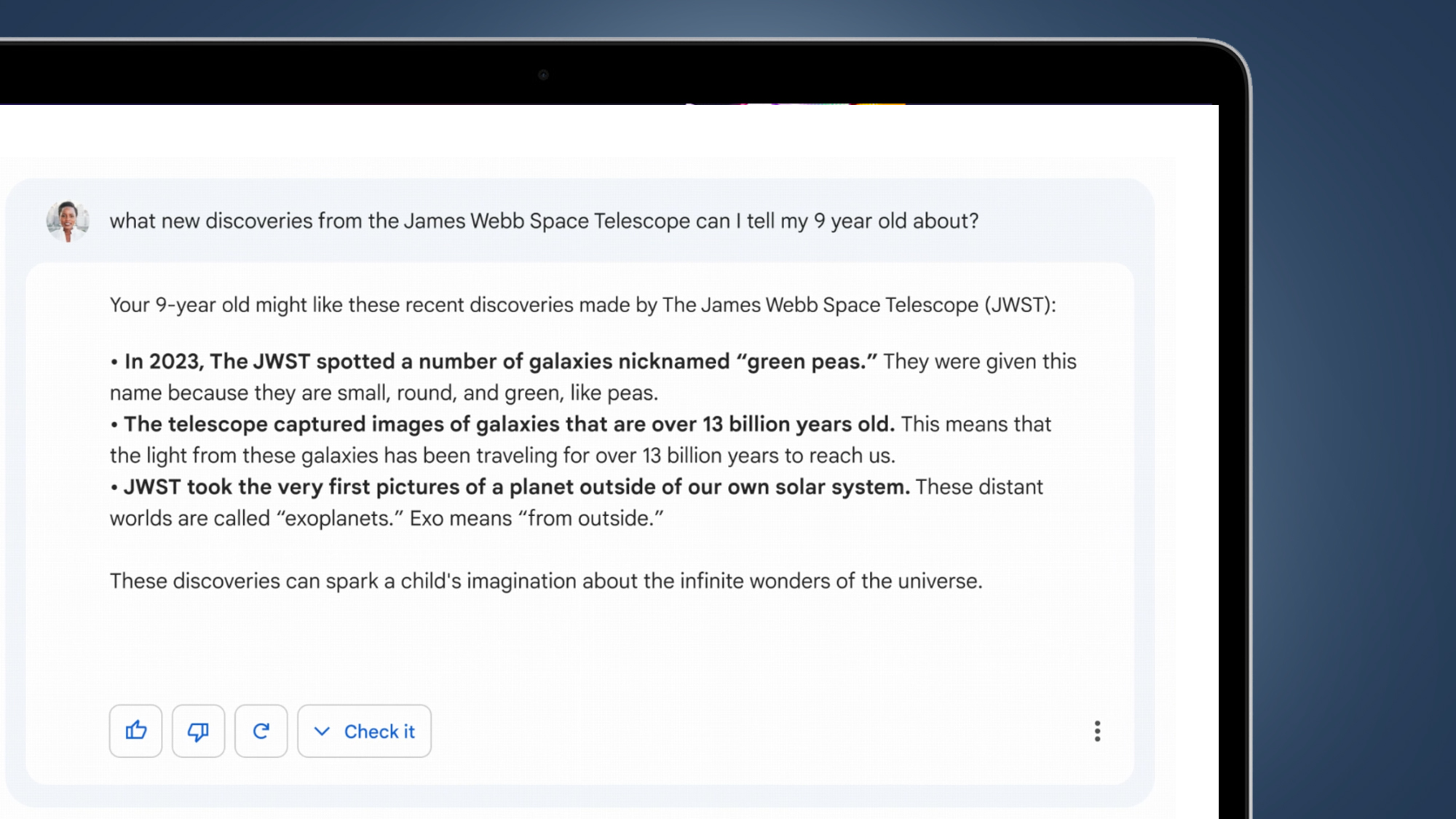
Google says that Bard can be “an outlet for creativity” or “a launchpad for curiosity, helping you to explain new discoveries from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to a 9-year-old, or learn more about the best strikers in football right now, and then get drills to build your skills”.
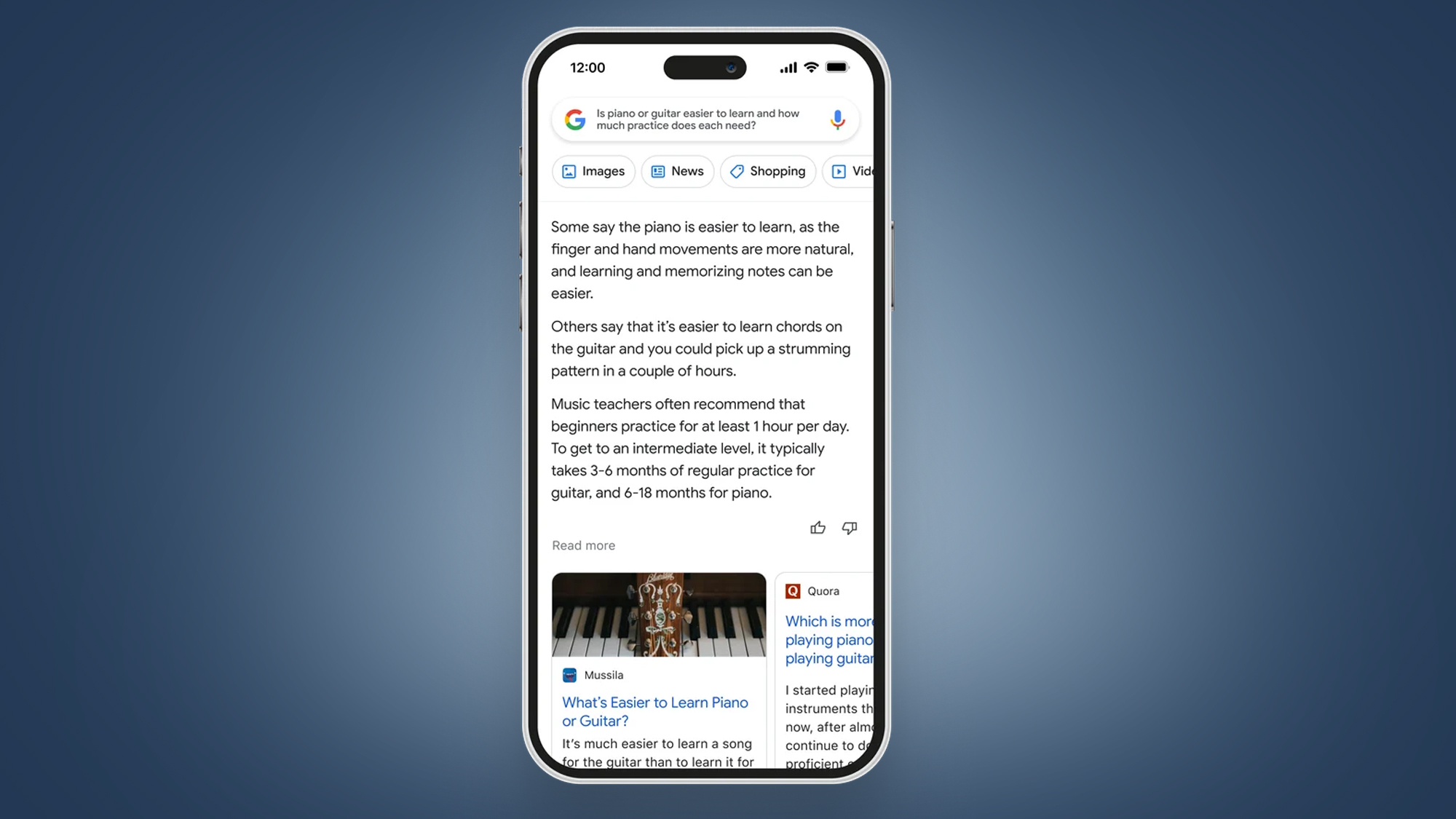
Unlike traditional Google Search, Bard draws on information from the web to help it answer more open-ended questions in impressive depth. For example, rather than standard questions like “how many keys does a piano have?”, Bard will be able to give lengthy answers to a more general query like “is the piano or guitar easier to learn”?
One of the biggest upgrades is PaLM 2, Bard’s language model and a direct answer to OpenAI’s GPT-4 model and what will be a foundation of Google’s AI products. It’s a massive general LLM with expanded reasoning, language, and coding capabilities. Smaller LLMs can and have been developed to tackle more precise and specialized tools, like Med-PaLM 2 and Sec-PaLM.
There’s also improved citations, meant to address the issue of misinformation and plagiarism. Bard will annotate a line of code or text that needs a citation, then underline the cited part and link to the source material. Bard will also let users export Python code through Replit in the near future, and will also increase language support from its current three to 40 languages.
A huge new feature coming soon is the ability for Google Bard to create generative images from text. This feature, a collaborative effort between Google and Adobe, will be brought forward by the Content Authenticity Initiative, an open-source Content Credentials technology that will bring transparency to images that are generated through this integration.
The whole project is made possible by Adobe Firefly, a family of creative generative AI models that will make use of Bard’s conversational AI service to power text-to-image capabilities. Users can then take these AI-generated images and further edit them in Adobe Express.
Google Bard vs ChatGPT: what’s the difference?
Fundamentally the chatbot is based on similar technology to ChatGPT, with even more tools and features coming that will close the gap between Google Bard and ChatGPT.
Both Bard and ChatGPT are chatbots that are built on ‘large language models’, which are machine learning algorithms that have a wide range of talents including text generation, translation, and answering prompts based on the vast datasets that they’ve been trained on.
The two chatbots, or “experimental conversational AI service” as Google calls Bard, are also fine-tuned using human interactions to guide them towards desirable responses. A potential difference between the two, though, is that ChatGPT isn’t currently connected to the internet, which means it has a very limited knowledge of facts or events after the year 2021.
Google says that Bard, meanwhile, “draws on information from the web” to provide up-to-date answers. This may not be a difference between Bard and ChatGPT for very long though — a leaked preview recently showed a version of Microsoft’s Bing with ChatGPT integration, which suggests that it won’t be long until we see the latter combined with Microsoft’s search engine.
Does Google Bard only do text answers?
Until recently Google’s Bard initially only answered text prompts with its own written replies, similar to ChatGPT. But one of the biggest changes to Bard is its multimodal functionality. This allows the chatbot to answer user prompts and questions with both text and images.
Users can also do the same, with Bard able to work with Google Lens to have images uploaded into Bard and Bard responding in text. Multimodal functionality is a feature that was hinted at for both GPT-4 and Bing Chat, and now Google Bard users can actually use it. And of course, we also have Google Bard’s Adobe-powered AI image generator, which will be powered by Adobe Firefly.

